You may be familiar with IP addresses labeling the location of a device, but do you know about port numbers? If you’re thinking to yourself, “I don’t even know where to find my port number,” don’t worry: you’re not alone.
Occasionally, finding your port number is necessary for ensuring that some applications are working as intended. Although it may sound complex, if you need to find your port number, the process is simple. Take a look at our guide below to find out more.
Understanding Ports and Port Numbers
Devices utilize ports as a way to connect different applications to the Internet simultaneously. Have you ever Googled an image, downloaded it to your computer, and printed it out from the same device? If so, you’ve successfully used three different ports to perform those tasks.
Port numbers are related to the processes performed by devices that are connected to the Internet. These numbers help facilitate the transfer of data between a device and a website or application. They act as an extension of your IP address and direct a protocol’s behavior to meet your device’s request.
Why Do You Need a Port Number?
Port numbers give you more control over how your software operates and interacts with the Internet. Each action on your device is tied to a different port. These port numbers come in a variety of labels, allowing them all to perform under the same IP address. Examples of common ports include:
- 0-1023: Well-known ports, used by large companies such as Apple
- 1024-49151: Registered ports, open to select services by request.
- 49152-65536: Private or dynamic ports, used temporarily or for private servers by anyone.
There are two distinct types of port numbers: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). These port numbers are similar in many ways, but they each vary in speed, security, and reliability.
Port numbers give you more control over how your software operates and interacts with the Internet.
PrivadoVPN
- TCP: TCP establishes endpoints when exchanging data, making it a more reliable port for guaranteeing the delivery of data packets. It also tracks the data to ensure that it doesn’t get lost. TCP is most commonly used on email apps and during web browsing.
- UDP: UDP doesn’t require you to establish a connection, making it less reliable but also faster. The data packets being exchanged through UDP aren’t monitored as thoroughly as they are with TCP. This means the data transfer is quicker, and UDP is used in places where speed is the most important factor.
Default Open Ports
Certain applications require specific open ports in order for them to operate properly. There is an ongoing list of registered ports available if you want to learn more. In most cases, however, you can use ports that are open by default, including:
- 20 – File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- 22 – Secure Shell (SSH)
- 25 – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- 53 – Domain Name System (DNS)
- 80 – Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- 110 – Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- 143 – Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- 443 – HTTP Secure (HTTPS)
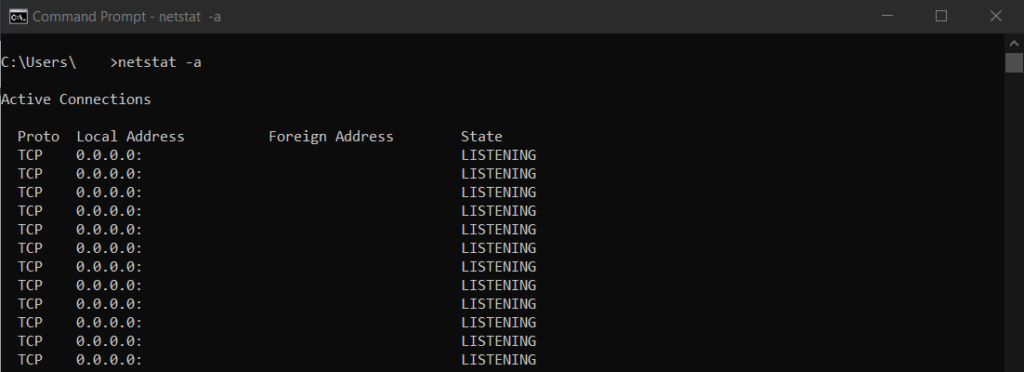
Find My Port Number on Windows
- Search “CMD” on your navigation bar and open Command Prompt.
- Next to “C:\Users\” and your name, type “netstat -a” and hit Enter.
- Your port numbers will be displayed below Active Connections.
Find My Port Number on Mac
- Press Command and Spacebar to open Spotlight.
- Search for “network utility” and hit enter.
- Select the Port Scan tab.
- Type the IP address you want to scan and click the Scan button.
- Open ports will generate in the lower half of the window.
How to Open a Port on Windows
- Search “Control Panel” on your navigation bar and open Control Panel.
- Click on System and Security, then select Windows Defender Firewall.
- On the menu, select Advanced settings.
- Click on Inbound Rules.
- Select New Rule.
- Click Port and then click the Next button.
- Select whether to use a TCP or UDP protocol.
- Add the port number beside Specific Local Ports, and click Next.
- Choose to Allow the Connection and click Next.
- Click the network rules for the port and select Next.
- Type the port name, a description of the port, and then click on Finish.
How to Open a Port on Mac
- Select the Apple icon and open your System Preferences.
- Open Security and Privacy and then select the Firewall tab.
- Click on Firewall Options.
- Select the plus sign icon to add a new application.
- Find an application on your device then click Add.
- Activate the function to “Allow Incoming Connections.”
- Select OK.
Secure Your Connection with PrivadoVPN
Cybercriminals can take advantage of the information they gather from your IP address and port number to steal your identity. Depending on your port settings, you can put yourself and your network at risk for cyber attacks. Open ports tend to have reduced security measures. This is why you need a reliable VPN on your network to help protect your data from prying eyes.
With PrivadoVPN, you can start to take back control of your privacy. Users can connect up to 10 devices on their accounts to ensure that everyone on the network is protected. Plus, with servers in 44+ countries, unlimited data, and a zero-log guarantee, PrivadoVPN makes it easy to ensure your privacy. No matter where you are or what device you use, PrivadoVPN can help take your privacy to the next level. Get started today and download the PrivadoVPN app now.
Get PrivadoVPN Today
Sign up for unlimited VPN data, access to SOCKS5 proxy,
and easy-to-use multi-device protection. Get started with PrivadoVPN now.




